33 results filtered with: Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in early anaphase. At this stage the chromosomes have started to separate from each other and move towardds opposite poles of the cell.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in anaphase
Matthew Daniels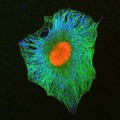
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell showing nucleus and tubulin
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Nucleus in prometaphase. The chromosomes are stained green. The chromatin has condensed but there is not yet complete attachment of the chromosomes to the spindle (not visible in the image).
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell early in cytokinesis
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Nucleus in late prophase
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in interphase showing the tubulin component of the cytoskeleton in green and the DNA in red. The centrosome, to which the microtubules attach, can be seen to the right of the nucleus.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Nucleus in early prophase
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes during cell division
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Nucleus in interphase. The large dark area is the nucleolus.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in telophase
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in metaphase. The chromatin is stained red and the "glue" that holds the two chromatids together is highlighted in yellow. This glue is a proteinaceous complex called cohesin. Once all the chromosomes are attached to the spindle, the cohesin complex breaks down, allowing the two chromatids to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in metaphase. The chromosomes are all aligned and at this stage they are attached to the spindle (not visible in this image).
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in early anaphase. At this stage the chromosomes have started to separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. The chromatin appears grey and the kinetochores are pink.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in interphase showing the tubulin component of the cytoskeleton in green, the DNA in blue and the kinetochores in pink.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in telophase. The chromosomes have separated and decondensed, and the new nuclear envelope forms.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cells showing the stages of cell division starting with interphase second from the left on the top. Progressing anticlockwise the stages shown are: early prophase (centrosome not yet separated), late prophase (centrosome separated and DNA condensation), prometaphase (incomplete chromosome attachment), metaphase (chromosomes all attached and aligned), anaphase (chromosome separation), telophase (formation of midbody and cells begin to flatten), early cytokinesis (chromosomes decondensed and nuclear envelope reformed) and late cytokinesis (cells move apart).
Matthew Daniels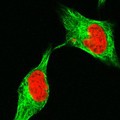
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell late in cytokinesis
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in metaphase
Matthew Daniels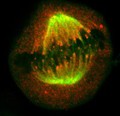
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in metaphase
Matthew Daniels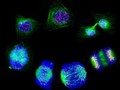
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cells showing the stages of cell division
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in telophase
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in anaphase
Matthew Daniels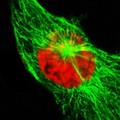
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in early prophase
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Two human cells in interphase. The microtubules are stained in green and the DNA in red.
Matthew Daniels